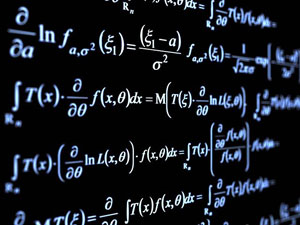Complex numbers arose in order to solve polynomial equations such as
or
which are not satisfied by real numbers. It’s assumed that a complex number has the form a + bi where a, b are real numbers and i, called imaginary unit, has the property that i2 = -1. Complex numbers are defined as follows.
- Addition.
- Subtraction.
- Multiplication.
- Division.
The ordinary rules of algebra has been used except that replaces i2 by -1 wherever it occurs. The commutative, associative and distributive laws also apply to complex numbers. It’s called a and b of a + bi the real and imaginary parts, respectively. Two complex numbers are equal if and only if their real and imaginary parts are respectively equal.
A complex number z = x + iy can be considered as a point P with coordinates (x, y) on a rectangular xy plane called in this case the complex plane or Argand diagram. If the line would be constructed from origin O to P and let ρ be the distance OP and φ the angle made by OP with the positive x axis, you could have from Figure
and could write the complex number in so-called polar form as
It’s often called that ρ the modulus or absolute value of of z and denote it by |z|. The angle φ is called the amplitude or argument of z abbreviated arg z. It could be also written
where
is called the conjugate of
.
If you write two complex numbers in polar form as
then
Also if n is any real number, you have
which is often called De Moivre’s theorem. You can use this to determine roots of complex numbers. For example if n is a positive integer,
Using the series for ex, sin x, cos x, you are led to define
which are called Euler’s formulas and which enable you to rewrite equations in terms of exponentials.
日: 2013年12月26日
複素数
複素数は や
といった実数解を持たない整方程式を解く際に出現します.複素数は a + bi という形をしており,a, b は実数部であり,i は虚数部と呼ばれ,i2 = -1 という性質を持ちます.複素数は以下のように定義されます.
- 加算
- 減算
- 乗算
- 除算
いかなる状況でも i2 を -1 で置換することを除けば,代数の通常の定義が用いられます.交換法則,結合法則,分配法則もまた複素数に適用されます.a + bi の a および b はそれぞれ 実数部 および 虚数部 と呼ばれます.二つの複素数が等しいとは,実数部と虚数部とがそれぞれ等しい時に限られます.
ある複素数 z = x + iy は xy 直交平面上の (x, y) 座標の点 P とみなすことができ,この場合この平面を 複素平面 または アルガン図 と呼びます.仮に原点 O から点 P への直線を引き,OP 間の距離を ρ とし,OP と x 軸のなす角度を φ とすると,次の図を得ます.
また複素数をいわゆる 極座標系式 として以下のように記述できます.
しばしば ρ は z の モジュラス または 絶対値 と呼ばれ,|z| と記述します.角 φ は z の amplitude または argument と呼ばれ,arg z と略記します. とも記述できます.ただし
は
の 共役複素数 と呼ばれます.
極座標で複素数を記述すると以下のようになります.
すると
仮に n を任意の実数とすると以下を得ます.
これは ド・モアブルの定理 として知られています.これを用いて複素数の根を定義できます.例えば仮に n を正の整数と仮定すると,
ex, sin x, cos x のための級数を用いると以下の定義に導かれます.
これらは オイラーの公式 と呼ばれ,方程式を指数関数の観点から書き直すことができます.