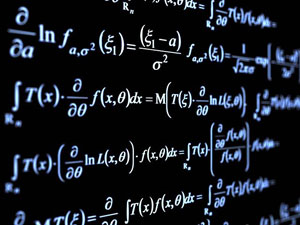- The value of a determinant remains the same if rows and columns are interchanged. In symbols,
.
- If all elements of any row [or column] are zero except for one element, then the value of the determinant is equal to the product of that element by its cofactor. In particular, if all elements of a row [or column] are zero the determinant is zero.
- An interchange of any two rows [or columns] changes the sign of the determinant.
- If all elements in any row [or column] are multiplied by a number, the determinant is also multiplied by this number.
- If any two rows [or columns] are the same or proportional, the determinant is zero.
- If we express the elements of each row [or column] as the sum of two terms, then the determinant can be expressed as the sum of two determinants having the same order.
- If we multiply the elements of any row [or column] by a given number and add to corresponding elements of any other row [or column], then the value of the determinant remains the same.
- If
and
are square matrices of the same order, then
- The sum of the products of the elements of any row [or column] by the cofactors of another row [or column] is zero. In symbols,
or
if

If
, the sum is
by (10).
- Let
represent row vectors [or column vectors] of a square matrix
of order n. Then
if and only if there exist constants [scalars]
not all zero such that

where O is the null or zero row matrix. If condition (13) is satisfied we say that the vectors
are linearly dependent. A matrix
such that
is called a singular matrix. If
, then
is a non-singular matrix.
In practice we evaluate a determinant of order n by using Theorem 7 successively to replace all but one of the elements in a row or column by zeros and then using Theorem 2 to obtain a new determinant of order n – 1. We continue in this manner, arriving ultimately at determinants of order 2 or 3 which are easily evaluated.
日: 2014年4月20日
行列式の定理
- 行列式の値は,行と列が入れ替わっても変化しません.記法では
.
- 任意の行または列の1つを除く全要素がゼロならば行列式の値は,そのゼロでない要素の余因子の積に等しくなります.特に,ある行または列の全要素がゼロならば行列式もゼロになります.
- 任意の 2 行または 2 列を交換すると行列式の符号が変化します.
- 任意の行または列の全要素にある数をかけると,その行列式もその数でかけられたものになります.
- 任意の 2 行または 2 列が同じか比例するならその行列式はゼロになります.
- 各行または各列の要素を 2 項で表現できるなら,その行列式は同次の二つの行列式の和で表現できます.
- 任意の行または列の要素にある数をかけ,任意の他の行または列の対応する要素に足していくと,その行列式の値は同じになります.
- 仮に
および
が同次の正方行列なら
- 他の行または列の余因子による任意の行または列の要素の積和はゼロとなります.記法では
or
if
仮に
なら
の和は (10) によります.
- ここで
が n 次正方行列
の行ベクトルまたは列ベクトルを表すとします.すると
となるのはすべてゼロではない以下の条件を満たす定数またはスカラー
が存在するときのみです.
ここで O はヌル行列または零行列です.仮に条件式 (13) が満たされるならベクトル
は 線形従属 であると示すことができます.ある行列
が
を満たすなら 特異行列 と呼びます.仮に
であるなら
は 非特異行列 です.
実際には,定理 7 によりある行または列の一つを除いた全要素を 0 で置換し,更に定理 2 を用いて n – 1 次の新しい行列式を得ることで n 次の行列式を評価できます.この方法を続けることで,最終的に 2 次または 3 次の行列式に到達するため,評価は容易です.