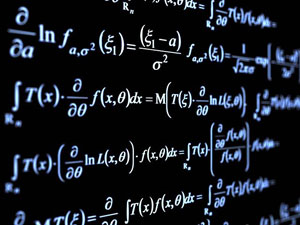If for a given square matrix
there exists a matrix
such that
, then
is called an inverse of
and is denoted by
. The following theorem is fundamental.
11. If
is a non-singular square matrix of order n [i.e.
], then there exists a unique inverse
such that
and we can express
in the following form
where
is the matrix of cofactors
and
is its transpose.
The following express some properties of the inverse:
日: 2014年4月21日
逆行列
仮にある正方行列 があって,
のような性質を有する
が存在するなら
は
の 逆行列 と呼ばれ
と記述します.下記の定理が成り立ちます.
11. 仮に が n 次の非特異的正方行列の場合,すなわち
の時,唯一のの逆行列
が存在し,
であって
を次の形で表現できます.
ここで は余因子
の行列であって
はその転置行列です.
以下は逆行列のいくつかの性質を示しています.