Theorem 12. The eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix [or symmetric real matrix] are real. The eigenvalues of a skew-Hermitian matrix [or skew-symmetric real matrix] are zero or pure imaginary. The eigenvalues of a unitary [or real orthogonal matrix] all have absolute value equal to 1.
Theorem 13. The eigenvectors belonging to different eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix [or symmetric real matrix] are orthogonal.
Theorem 14. [Cayley-Hamilton] A matrix satisfies its own characteristic equation.
Theorem 15. [reduction of matrix to diagonal form] If a non-singular matrix
has distinct eigenvalues
with corresponding eigenvectors written as columns in the matrix
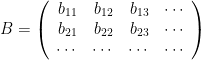
then

i.e.
, called the transform of
by
, is a diagonal matrix containing the eigenvalues of
in the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. We say that
has been transformed or reduced to diagonal form.
Theorem 16. [Reduction of quadratic form to canonical form] Let
be a symmetric matrix, for example,
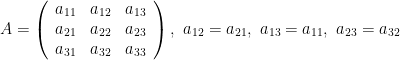
Then if
, we obtain the quadratic form
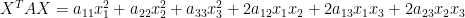
The cross product terms of this quadratic form can be removed by letting
where
is the column vector with elements
and
is an orthogonal matrix which diagonalizes
. The new quadratic form in
with no cross product terms is called the canonical form. A generalization can be made to Hermitian quadratic forms.
日: 2014年4月27日
固有値と固有ベクトルにおける定理
定理 12. エルミート行列(または実対称行列)の固有値は実数です.歪エルミート行列(または歪対称実行列)の固有値はゼロまたは純虚数です.ユニタリ行列(または実直交行列)の固有値はすべて絶対値は 1 に等しくなります.
定理 13. エルミート行列(または実対称行列)の異なる固有ベクトルに属する固有ベクトルは直交します.
定理 14. (ケーリー・ハミルトン) ある行列は自身の特性方程式を満たします.
定理 15. (対角形への行列の縮約) ある正則行列 に明確な固有値
があって対応する固有ベクトルが行列の中で列として記述されるなら
すると
すなわち は
による
の 変換 と呼び,
の固有値を主対角線上に持ち,他はすべてゼロの対角行列です.
は 変換された または 対角形に縮約された といいます.
定理 16. (二次形式の標準形への縮約) を対称行列とします.例えば
すると仮に ならば 二次形式 が得られます.
この二次形式の外積の項は と置くことで除去されますが,ここで
は
の要素を持つ列ベクトルです.また
は直交行列で
を直交化したものです.
における新しい二次形式には外積の項がなく 標準形 と呼びます.一般化はエルミート二次形式によりなされます.