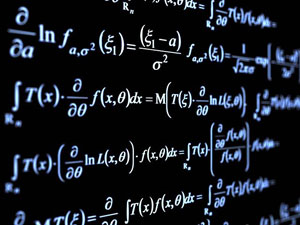If for a given square matrix
there exists a matrix
such that
, then
is called an inverse of
and is denoted by
. The following theorem is fundamental.
11. If
is a non-singular square matrix of order n [i.e.
], then there exists a unique inverse
such that
and we can express
in the following form
where
is the matrix of cofactors
and
is its transpose.
The following express some properties of the inverse:
Inverse of a matrix