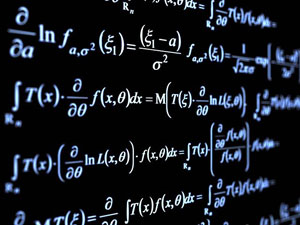Let
be a closed surface bounding a region of volume
. Choose the outward drawn normal to the surface as the positive normal and assume that
are the angles which this normal makes with the positive
,
and
axes respectively. Then if
and
are continuous and have continuous partial derivatives in the region
which can also be written
In vector form with
and
, these can be simply written as
In words this theorem, called the divergence theorem or Green’s theorem in space, states that the surface is equal to the integral of the normal component of a vector
taken over a closed surface is equal to the integral of the divergence of
taken over the volume enclosed by the surface.
THE DIVERGENCE THEOREM